
WordPress is loaded with tools that enable you to personalize and run your website. However, configuring the right settings early on can save you a lot of time in the future. In this guide, we will look at the critical settings of WordPress that are available for all users — General , Writing, Reading, Discussion, Media, and Permalinks.
The General Settings is a section where you set the basic details about your site.
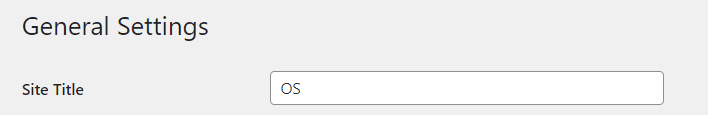
Site Title: This is the name of your website, displayed in the browser tab and used for SEO.
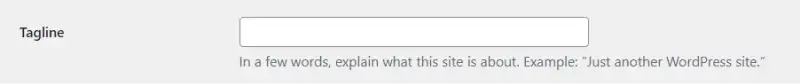
Tagline: A short description or slogan that complements your site title.
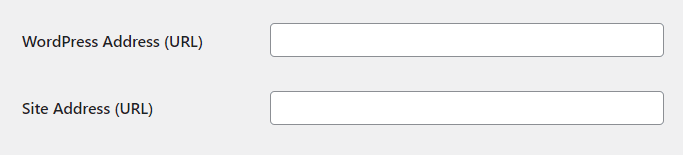
WordPress Address (URL) and Site Address (URL): These define your website's address. They should match unless you have specific reasons to separate them.
Email Address: The admin email for receiving notifications.
Membership: Check the "Anyone can register" box if you allow users to create accounts on your site. Use this only for sites that require user registrations, like forums or e-commerce platforms.

New User Default Role: Assign the default role for new users (e.g., Subscriber for limited access).

Timezone, Date, and Time Format: Set the correct timezone and formatting for your site's location.
The Writing Settings control how you create and publish content.
Default Post Category: Select the category that posts will default to if you don't manually assign one.

Default Post Format: Choose the format for your blog posts (e.g., Standard, Gallery, Video). Most blogs stick to Standard.

Email Posting: (deprecated in newer versions): Used for posting via email. This is now rarely used due to more modern alternatives.
Update Services: Ping services like Pingomatic to notify search engines when you publish new content. This is helpful for improving SEO.
The Reading Settings determine how your site's content is displayed to visitors.
Your Homepage Displays:
Posts Page: If you set a static homepage, assign a different page to display your blog posts.
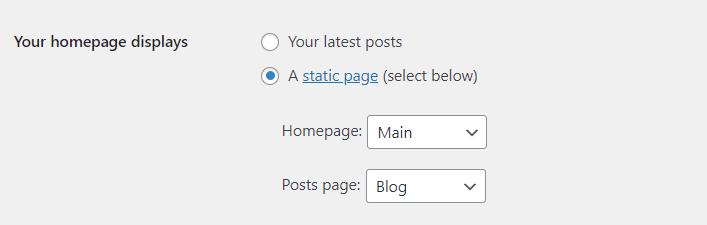
Blog Pages Show at Most: Set the number of posts shown per page on your blog.
Syndication Feeds Show the Most Recent: Determines the number of posts shown in your RSS feed.

For Each Post in a Feed, Include:
Full text: Displays the entire post in RSS feeds.
Summary: Shows only an excerpt.

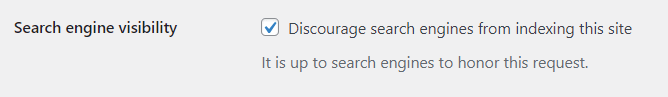
Search Engine Visibility: Check this box to discourage search engines from indexing your site while it's under development.
The Discussion Settings control how comments are managed on your site.
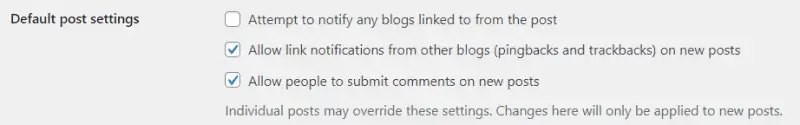
Default Post Settings:
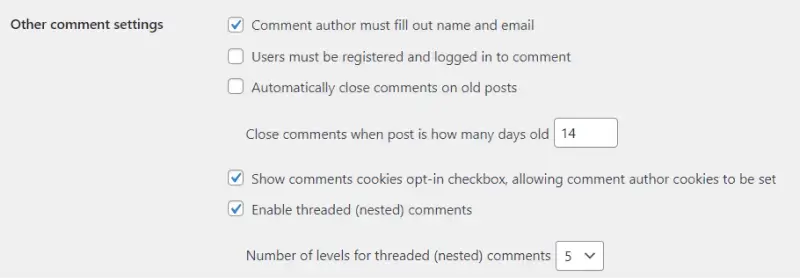
Other Comment Settings:
Email Me Whenever:
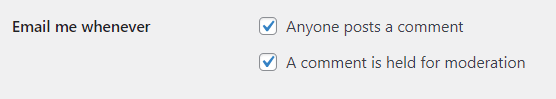
Before a Comment Appears: Hold a comment in the moderation queue if it contains links or specific keywords.

Avatars: Enable or disable profile pictures for commenters. Use the Gravatar service or a custom option.
The Media Settings manage how images and other media files are handled.
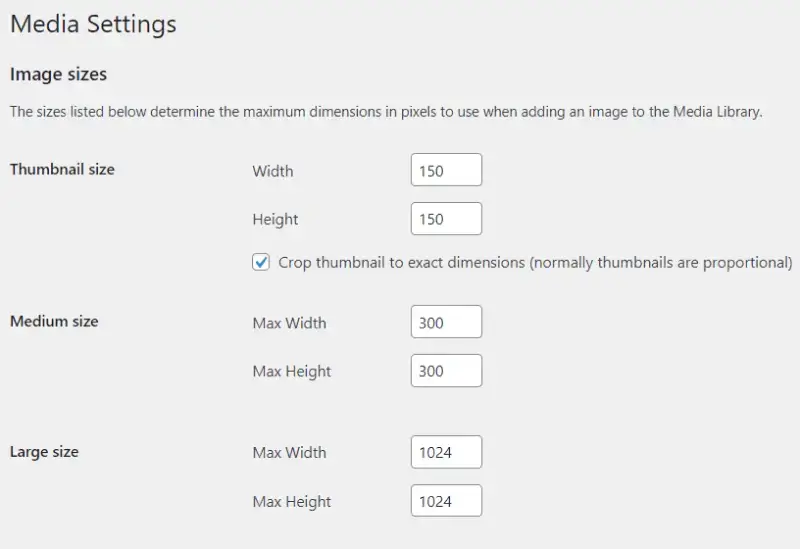
Thumbnail, Medium, and Large Image Sizes: Set dimensions for these standard image sizes. These sizes are automatically generated when you upload an image.
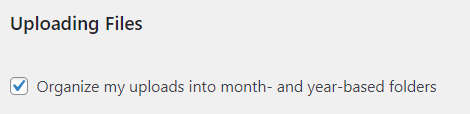
Uploading Files: Organize your uploads into month- and year-based folders for better management.
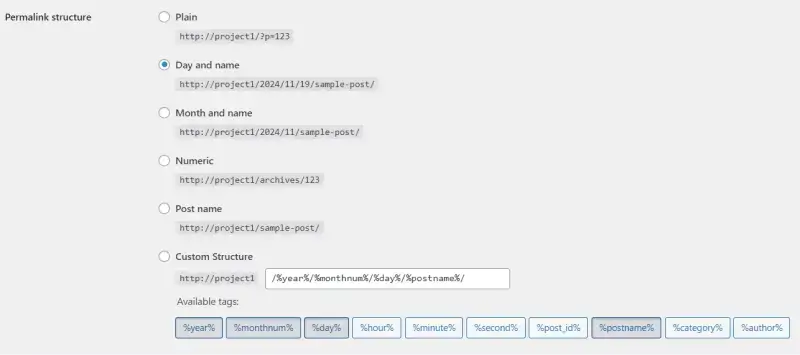
The Permalink Settings define your site's URL structure. A clean and descriptive URL is essential for SEO.
Common Settings:
Custom Structure: Create a custom format by combining tags like `/category/post-name/`.
Recommended: Post Name for blogs and SEO-friendly URLs.
Configuring your WordPress settings is an important step in building a functional, user-friendly, and secure website. By adjusting these settings to suit your needs, you can create a smooth experience for both yourself and your visitors. Always revisit your settings periodically, especially after major WordPress updates or changes to your website's purpose.
Other Worpress Articles that may be interesting for you: